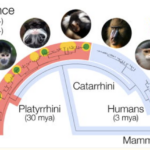
Unique Human Sialic Cell Biology Is Shared by New World Primates
Parallel Evolution of a Self-Signal: Humans and New World Monkeys Independently Lost the Cell Surface Sugar Neu5Gc Springer, Stevan A., Sandra L, Diaz, and Pascal Gagneux. Immunogenetics. 2014 Aug 16;66(11):671–674. doi: 10.1007/s00251-014-0795-0 Human sialic acid biology is unusual and thought…

MARMOSETS SHOW A PHONO-ARTICULATORY RHYTHM CHARACTERISTIC OF HUMAN SPEECH
Theta Synchronization of Phonatory and Articulatory Systems in Marmoset Monkey Vocal Production Risueno-Segovia, Cristina, and Steffen R. Hage. Current Biology. 2020 Nov 2;30(21):4276-4283.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2020.08.019. Abstract Human speech shares a 3-8-Hz theta rhythm across all languages [1-3]. According to the…
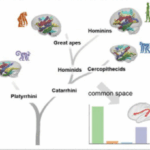
MARMOSET VOCALIZATION IS CLOSER TO HUMANS THAN TO OLD WORLD PRIMATES (CHIMPS AND MACAQUES)
Evolutionary Convergence of the Arcuate Fasciculus in Marmosets and Humans Wang, Yufan, Luqi Cheng, Deying Li, Yuheng Lu, William D. Hopkins, Chet C. Sherwood, Ting Xu, Cirong Liu, George Paxinos, Tianzi Jiang, Congying Chu, and Lingzhong Fan. Abstract The marmoset is a highly vocal platyrrhine monkey that shares key anatomical and…
Only human and marmoset babies babble
Altricial brains and the evolution of infant vocal learning Biazzi, Renata B., Daniel Y. Takahashi, and Asif A. Ghazanfar Abstract Vocal development in human infants is strongly influenced by interactions with caregivers who reinforce more speech-like sounds. This trajectory of vocal development in humans…


Recent Comments