Unique Human Sialic Cell Biology Is Shared by New World Primates
Parallel Evolution of a Self-Signal: Humans and New World Monkeys Independently Lost the Cell Surface Sugar Neu5Gc
Springer, Stevan A., Sandra L, Diaz, and Pascal Gagneux.
Immunogenetics. 2014 Aug 16;66(11):671–674. doi: 10.1007/s00251-014-0795-0
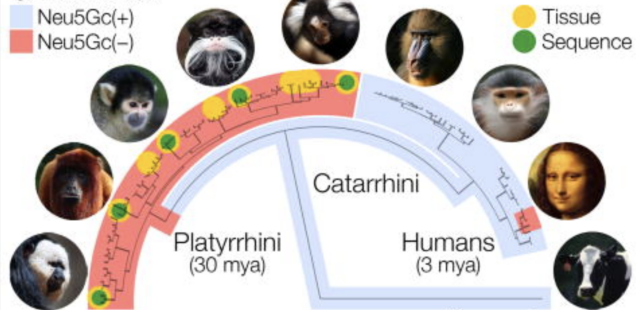
Human sialic acid biology is unusual and thought to be unique among mammals. Humans lack a functional CMAH protein and cannot synthesize the sugar Neu5Gc, an innate mammalian signal of self. Losing this sugar changed how humans interact with some of our deadliest pathogens: malaria, influenza and streptococcus among others. We show that the New World monkeys, comprising a third of all primate species, have human-like sialic acid biology. They have lost Neu5Gc because of an independent CMAH inactivation ∼30 million years ago (compared to ∼3 mya in hominids). This parallel loss of Neu5Gc opens sialic acid biology to comparative phylogenetic analysis, and reveals an unexpected conservation priority. New World Monkeys risk infection by human pathogens that can recognize cells in the absence of Neu5Gc. This striking molecular convergence provides a mechanism that could explain the longstanding observation that New World monkeys are susceptible to some human diseases that cannot be transmitted to other primates.


Keep it up, there is more than just a coincidence.
Tyranny of Ideas
“In view of these conditions, the theory of AN AUTOCHTHONOUS ORIGIN OF THE AMERICAN RACE MAY BE SET ASIDE, and the problem of the ARRIVAL in the New World of racial elements originating in the Old World need ALONE receive CONSIDERATION.” (Willian Henrey Holmes, 1912) pp. 30-31 all EMPHASIS added AMH
This one line sums up ‘that we had it right’ and ‘why we got it wrong.’